-
Please select a product category
-
Products:
Show overview -
Mobile Filter Units

- back | Mobile Filter Units
- Mobile Filter Units: Show overview
-
SmartMaster
 Disposable filter - 13 m²
Disposable filter - 13 m² -
ProfiMaster
 Disposable filter - 17 m²
Disposable filter - 17 m² -
SmartFil
 Disposable filter - 25 m²
Disposable filter - 25 m² -
MaxiFil
 Disposable filter - 42 m²
Disposable filter - 42 m² -
MaxiFil Active Carbon
 Disposable filter - 34 m²
Disposable filter - 34 m² -
FilterMaster XL
 Automatic filter cleaning
Automatic filter cleaning -
MaxiFil Clean
 Automatic filter cleaning
Automatic filter cleaning -
Replacement filter
 For mobile devices
For mobile devices- back | Replacement filter
- Replacement filter: Show overview
-
Spare filter for SmartMaster
 Disposable filter - 13 m²
Disposable filter - 13 m² -
Spare filter for ProfiMaster
 Disposable filter - 17 m²
Disposable filter - 17 m² -
Replacement filter for SmartFil
 Disposable filter - 25 m²
Disposable filter - 25 m² -
Replacement filter for MaxiFil
 Disposable filter - 42 m²
Disposable filter - 42 m² -
Set Main filter and activated charcoal filter for ...

-
Spare filter for MaxiFil

-
Activated charcoal filter

-
Replacement filter for FilterMaster XL
 KemTex® ePTFE - 10 m²
KemTex® ePTFE - 10 m² -
Spare filter for Cartridge Filter
 KemTex® ePTFE - 15 m²
KemTex® ePTFE - 15 m² -
Dust collection cartridge MaxiFil Clean (Set of 4)

-
Stationary Extraction Systems

- back | Stationary Extraction Systems
- Stationary Extraction Systems: Show overview
-
WallMaster
 Disposable filter - 42 m²
Disposable filter - 42 m² -
MaxiFil stationary
 Disposable filter - 42 m²
Disposable filter - 42 m² -
FilterTable
 Disposable filter - 16 m²
Disposable filter - 16 m² -
FilterTable GWT
 Disposable filter - 15,8 m²
Disposable filter - 15,8 m² -
Cartridge Smoke Filter Unit Stationary
 Automatic filter cleaning
Automatic filter cleaning -
Cartridge Smoke Filter Unit Stationary
 Automatic filter cleaning
Automatic filter cleaning -
FilterCell XL
 Automatic filter cleaning
Automatic filter cleaning
-
Central Extraction Systems

-
High-vacuum Extraction

-
General Ventilation Systems

- back | General Ventilation Systems
- General Ventilation Systems: Show overview
-
CleanAirTower SF 9000
 Storage filter - 100 m²
Storage filter - 100 m² -
AirDome

-
CleanAirTower
 Automatic filter cleaning
Automatic filter cleaning -
KemJet
 General Ventilation System
General Ventilation System -
System Push-Pull

-
Displacement Ventilation
-
Air Monitoring System AirWatch
 Traffic light red - yellow - green
Traffic light red - yellow - green -
Dustlight
 Air monitoring directly on the body
Air monitoring directly on the body -
KEMPER Connect
 The digital IoT platform
The digital IoT platform
-
Exhaust Arms And Fans

- back | Exhaust Arms And Fans
- Exhaust Arms And Fans: Show overview
-
Exhaust Arms
 Various arm lengths
Various arm lengths -
Fans

-
Exhaust air set
 All-In-One
All-In-One -
Exhaust hoods
 Maximum suction power
Maximum suction power- back | Exhaust hoods
- Exhaust hoods: Show overview
-
The Hood Pro

-
The Hood

-
Extraction And Cutting Tables

- back | Extraction And Cutting Tables
- Extraction And Cutting Tables: Show overview
-
Extraction Tables For Manual Applications

- back | Extraction Tables For Manual Applications
- Extraction Tables For Manual Applications: Show overview
-
Grinding Tables

-
Welding Fume Extraction Tables

-
FilterTable GWT
 Disposable filter - 15,8 m²
Disposable filter - 15,8 m² -
Welding Fume Extraction Tables With Fan

-
FilterTable Extraction

-
Hand Cutting Extraction Tables

-
Hand Cutting Extraction Table With Fixture

-
Welding Smoke Extraction Training Tables

-
Training table with forced position welding ...

-
Fume Extraction Tables For Cutting Systems

- back | Fume Extraction Tables For Cutting Systems
- Fume Extraction Tables For Cutting Systems: Show overview
-
KemTab
 up to 300 Ampere
up to 300 Ampere -
KemTab Advance
 up to 300 Ampere
up to 300 Ampere
-
Occupational safety and partition walls

- back | Occupational safety and partition walls
- Occupational safety and partition walls: Show overview
-
Welding Protection Curtain

-
Welding strip curtains

-
Welding protection strips

-
Welding protectors

- back | Welding protectors
- Welding protectors : Show overview
-
1-panel mobile protective screen with curtain

-
1-panel mobile protective screen with curtain

-
1-Panel Mobile Protective Screen With Strip ...

-
1-Panel Mobile Protective Screen With Strip ...

-
3-Panel Mobile Protective Screen With Curtain

-
3-Panel Mobile Protective Screen With Strip ...

-
3-Panel Mobile Protective Screen With Strip ...

-
Wheel set

-
Welding protective blankets

- back | Welding protective blankets
- Welding protective blankets: Show overview
-
Welding Blanket 750°C

-
Welding Blanket 950 °C

-
Welding Blanket 1.350°C

-
Sound Insulating Partitioning Wall Systems

-
Mobile soundproof wall

-
Pivoting arm, wall-mounted or with column
- back | Pivoting arm, wall-mounted or with column
- Pivoting arm, wall-mounted or with column: Show overview
-
Pivoting Arm
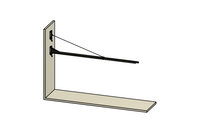
-
Pivoting Arm

-
Pivoting Arm Including Column
-
Pivoting Arm Including Column
-
Swivel Arm

-
Hoses

-
Please select a page
-
Worth knowing:
Show overview -
Weldings fumes in general

-
Regulations of welding fumes

- back | Regulations of welding fumes
- Regulations of welding fumes: Show overview
-
1. Overview

-
2. Hazard Assessment

-
3. Measures of fume extraction

-
4. Effectiveness check
-
Extraction unit - Overview of applications

- back | Extraction unit - Overview of applications
- Extraction unit - Overview of applications: Show overview
-
Mobile Extraction Systems - Area of application

-
Mobile Extraction Systems - selection criteria

-
Stationary Extraction Systems - application area

-
Stationary Extraction Systems - selection criteria

-
Zentrale Absauganlage - Filteranlage Überblick

- back | Zentrale Absauganlage - Filteranlage Überblick
- Zentrale Absauganlage - Filteranlage Überblick: Show overview
-
Central Extraction Systems - overview

-
Central Extraction Systems in detail

-
Accessories for central extraction units

-
IFA W3 examination for central filter unit

-
Surface filtration Filter cartridges
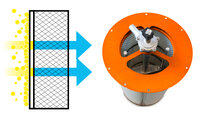
-
General ventilation system

-
Exhaust arm overview
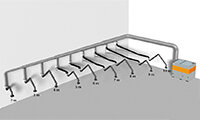
-
Extraction table - cutting table

-
Please select a page
-
Current topics:
Show overview -
News

-
Trade fairs

-
Luftreiniger AirCO2NTROL

-
Please select a page
-
Blog:
Show overview
-
Please select a page
-
Services:
Show overview -
Catalogue order

-
Downloads

-
Product registration

-
Videos

-
Please select a page
-
Downloads:
Show overview
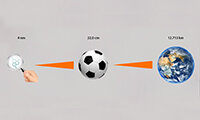
Physical effects by absorbing pollutants in welding fumes
The occurring pollutants have to be distinguished into 3 types:
- Substances that place strain on respiratory tract and lungs
- Toxic or poisonous substances
- Carcinogenic substances
Substances that place strain on respiratory tract and lungs
For example:
- Iron oxides
- Aluminum oxides
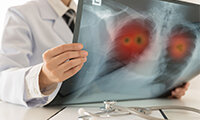
If exposed for a long period and if the concentration is high, then these substances can cause strain to the respiratory tract and the lungs.This can lead to respiratory illnesses such as (chronic) bronchitis or asthma and deposits of metals in the lungs (siderofibrosis, aluminosis).
Toxic or poisonous substances
For example:
- Prussic acid
- Carbon monoxide / carbon dioxide
- Chrome III compounds
- Manganese oxide
These substances cause poisoning if a certain dose is exceeded within the Body. Their toxic effect may e.g. prevent oxygen supply to the blood. Other symptoms may be:
- Irritation to mucous membranes and respiratory tract
- Respiratory paralysis or strong acceleration of breathing and pulse
- Headaches, tiredness and dizziness including fainting
- Nausea
- Pulmonary oedema (water oedema in the lung) which may cause death
Some of these substances are also suspected to have a carcinogenic effect.
Carcinogenic substances
For example:
- Chrome (VI)-compounds
- Various oxides (prussic acid, beryllium oxide, nickel oxide)
Carcinogenic substances can result in malignant Tumors. An growing dose of these substances increases the risk of cancer. These substances frequently also have a toxic effect.
>> to 1. Welding fumes - What are they?
>> to 2. Composition of welding fumes
>> to 3. How large are the individual particles in welding fumes?
Search Kemper.eu
Use the search box below to search for products, services and information on Kemper.eu.
CloseHow may we contact you?
Just fill out the form. We will contact you as soon as possible.